Description :
The apricot is a small tree, 8–12 m (26–39 ft) tall, with a trunk up to 40 cm (16 in) in diameter and a dense, spreading canopy. The leaves are ovate, 5–9 cm (2.0–3.5 in) long, and 4–8 cm (1.6–3.1 in) wide, with a rounded base, a pointed tip, and a finely serrated margin. The flowers are 2–4.5 cm (0.8–1.8 in) in diameter, with five white to pinkish petals; they are produced singly or in pairs in early spring before the leaves. The fruit is a drupe similar to a small peach, 1.5–2.5 cm (0.6–1.0 in) diameter (larger in some modern cultivars), from yellow to orange, often tinged red on the side most exposed to the sun; its surface can be smooth (botanically described as: glabrous) or velvety with very short hairs (botanically: pubescent). The flesh is usually firm and not very juicy. Its taste can range from sweet to tart. The single seed is enclosed in a hard, stony shell, often called a "stone" or "kernel", with a grainy, smooth texture except for three ridges running down one side.
Species :
Apricots are species belonging to Prunus sect. Armeniaca. The taxonomic position of P. brigantina is disputed. It is grouped with plum species according to chloroplast DNA sequences,but more closely related to apricot species according to nuclear DNA sequences.
- Prunus armeniaca – common apricot, widely cultivated for its edible fruit and kernel
- Prunus brigantina – Briançon apricot, native to Europe, cultivated for its edible fruit and oil-producing kernel
- Prunus cathayana - native to Hebei
- Prunus dasycarpa – purple apricot, cultivated in Central Asia and adjacent areas for its edible fruit
- Prunus hongpingensis – Hongping apricot, native to Shennongjia, cultivated for its edible fruit
- Prunus hypotrichodes – native to Chongqing
- Prunus limeixing – cultivated in northern China for its edible fruit
- Prunus mandshurica – Manchurian apricot, native to Northeast Asia, cultivated for its kernel, the fruits of some cultivars edible
- Prunus mume – Japanese apricot, native to southern China, widely cultivated for its beautiful blossom and edible fruit
- Prunus sibirica – Siberian apricot, native to Siberia, Mongolia, northern China, and Korea, cultivated for its kernel
- Prunus zhengheensis – Zhenghe apricot, native to Fujian
Production :
In 2019, world production of apricots was 4.1 million tonnes, led by Turkey with 21% of the world total. Other major producers (in descending order) were Uzbekistan, Iran, Italy, and Algeria.
Dried Apricot :
Dried apricots are a type of traditional dried fruit. The world's largest producer of dried apricots is Turkey.When treated with sulfur dioxide (E220), the color is vivid orange. Organic fruit not treated with sulfur dioxide is darker in color and has a coarser texture. When apricots are dried, the relative concentration of nutrients is increased, with vitamin A, vitamin E, potassium, and iron having Daily Values above 25%.
Nutrition :
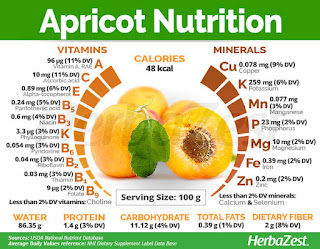
In a 100-gram amount, raw apricots supply 48 Calories and are composed of 11% carbohydrates, 1% protein, less than 1% fat, and 86% water. Raw apricots are a moderate source of vitamin A and vitamin C (12% of the Daily Value each).
Apricots are nutritious and contain numerous fundamental nutrients and minerals.
Only 2 new apricots (70 grams) give:- Calories: 34
- Carbs: 8 grams
- Protein: 1 gram
- Fat: 0.27 grams
- Fiber: 1.5 grams
- Vitamin A: 8% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Vitamin C: 8% of the DV
- Vitamin E: 4% of the DV
- Potassium: 4% of the DV
Moreover, this organic product is a nice wellspring of beta carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin, which are all strong cancer prevention agents that assistance battle free extremists in your body. It's ideal to appreciate apricots entire and unpeeled, as the skin brags huge sums fiber and supplements. Make certain to dispose of the stone, as it's unpalatable.
High in cell reinforcements :
Apricots are an incredible wellspring of numerous cancer prevention agents, including beta carotene and Vitamin A, C, and E. Furthermore, they're high in a gathering of polyphenol cell reinforcements called flavonoids, which have been appeared to secure against ailments, including diabetes and coronary illness. The fundamental flavonoids in apricots are chlorogenic acids, catechins, and quercetin.
These mixtures work to kill free revolutionaries, which are hurtful mixtures that harm your cells and cause oxidative pressure. Oxidative pressure is connected to heftiness and numerous persistent illnesses, like coronary illness. In one examination in 2,375 individuals, scientists fostered a scoring framework to quantify changes in degrees of provocative markers. They tracked down that high flavonoid and anthocyanin admissions were related with a 42% and 73% lower aggravation score, separately. High flavonoid admission was likewise attached to a 56% lower oxidative pressure score.
May support skin wellbeing :
Eating apricots may profit your skin. The primary driver of wrinkles and skin harm are ecological variables, like the sun, contamination, and tobacco smoke. Additionally, research demonstrates an immediate connection between bright (UV) light openness, burns from the sun, and your danger of melanoma, a lethal type of skin disease. Vitamin C and E, both found in this natural product, may help your skin. Specifically, nutrient C ensures against UV harm and natural contaminations by killing free revolutionaries.
High in potassium :
Apricots are high in potassium, a mineral that additionally fills in as an electrolyte. In your body, it's answerable for conveying nerve messages and managing muscle withdrawals and liquid equilibrium.
Two apricots (70 grams) give 181 mg of this mineral, which is 4% of the DV.
May secure your liver :
Some information recommends that apricots may help shield your liver from oxidative pressure. In two creature considers, rodents took care of liquor and apricots had lower levels of liver catalysts and markers of aggravation than rodents given liquor however no apricots.
Simple to add to your eating regimen :
Both new and dried apricots make for a speedy, delightful tidbit or a simple expansion to your #1 supper. You can add them to your eating routine in an assortment of ways, including:
- Mixed into trail blend or granola.
- Eaten new as a bite.
- Cut and added to yogurt or salad.
- Utilized in jams, jelly, and salsas.
- Stewed in a sluggish cooker with meat, like chicken or hamburger.
- Added to sweets like pies, cakes, and baked goods.
Benefits :
- Health Benefit
On account of their high measure of Vitamin, flavonoids, and potassium, apricots have huge medical advantages.
Flavonoids work to ensure and reinforce your veins while diminishing indications of irritation. Potassium, a significant mineral for nerve and muscle work, is additionally urgent for assisting supplements with moving around the body. Furthermore, it upholds solid pulse and heart wellbeing. Here are a couple of more medical advantages of apricots:
- Skin Protection
Cancer prevention agents like nutrient E and nutrient C are known for their skin-boosting properties. They can assist with shielding skin cells from bright (UV) radiation, diminish indications of early wrinkles, and improve skin flexibility. Beta-carotene is another cell reinforcement that assists with shielding your skin from burns from the sun and extra UV harm. Since apricots have high water content, they're additionally a decent method to hydrate your skin. One cup of apricots offers around 2/3 of some water.
- Solid Vision
Rich in Vitamin A, beta-carotene, and different carotenoids, apricots are great for advancing eye wellbeing. Lutein assists with supporting retina and focal point wellbeing, while carotenoids and nutrient E support generally speaking vision. Apricot supplements likewise help to diminish the danger of macular degeneration and waterfalls.
- Better Digestion
Apricots offer a lot of good dietary fiber to help your stomach related lot. Their complete fiber content is about half solvent fiber and half insoluble fiber. Solvent fiber assists your stomach related lot with holding water and urges great microscopic organisms to flourish. Insoluble fiber is additionally useful for sound gut microorganisms levels.